Attribution Theory
Table of Contents
- Locus
- Stability
- Controllability
Essentially, attribution theory deals with how we attach meaning to other's behavior, or our own? For example, is someone angry because they are bad-tempered or because something bad happened. Attribution theory also deals with how well we control the factors involved?
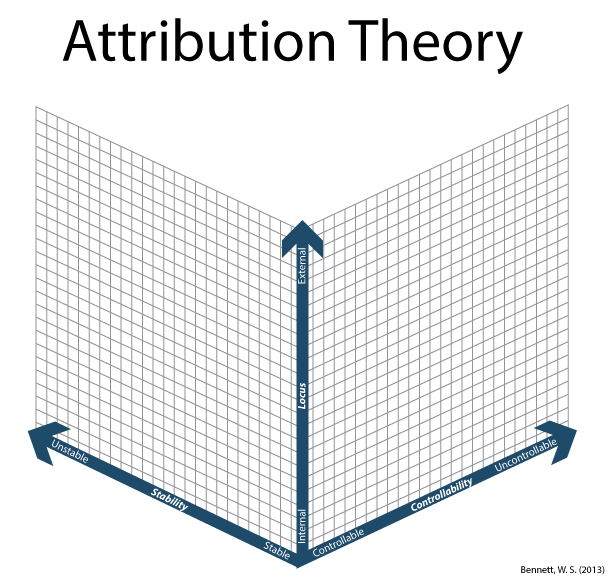 Figure 1. Conceptual model of attribution theory based on Weiner (1985).
Figure 1. Conceptual model of attribution theory based on Weiner (1985).
Locus
Also known as Locus of Control, refers to a person's state of mind regarding whether or not they believe that their actions control their own outcomes in life.
Stability
The amount of stability of attribution. Are a person's attributions stable or in flux.
Controllability
How much control a person has with regard to their attribution. Are they able to control it or is it becoming uncontrollable.